Before PHP 5.4, a new version of PHP was published when enough core developers agreed that it was ready for release. This situation was dissatisfying for everyone involved. Vendors of operating system distributions, for instance, did not know when a new version of PHP would be released and could not plan for it until after it was published.
The PHP project adopted a new release process in 2012. Or rather, it introduced a formal release process for the first time to put an end to the chaotic release practice of the past. A new minor version such as PHP 7.1 is released every year. Each such minor version has a well-defined, three-year lifecycle:
- Active Support: A minor version is actively supported for two years after its initial release. During this time, reported bugs and security issues are fixed, and regular point releases are made.
- Security Support: After two years of active support, a minor release is supported for critical security issues only, and releases are no longer made on a regular basis. This security support ends three years after the initial release of the minor version.
PHP 5.6 was released on August 28, 2014. As it is the final minor version of PHP 5, the active support for PHP 5.6 was extended by four months and its security support was extended by an additional year.
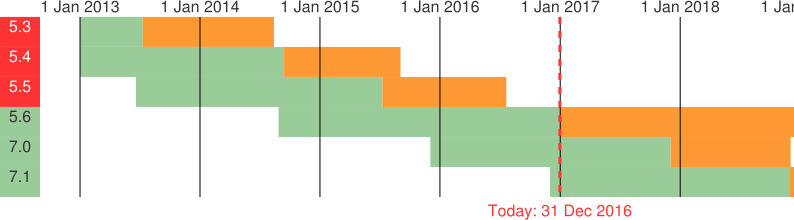
PHP 5.6.30, due in early January 2017, will be the final release of PHP 5.6 that contains regular bug fixes. After PHP 5.6.30 and until December 31, 2018, only critical security issues will still be fixed for PHP 5.6 and releases will be made on an as-needed basis. Users of PHP 5 should upgrade to PHP 7 as soon as possible, as they may be exposed to unpatched security vulnerabilities after December 31, 2018 when PHP 5 reaches its End of Life.
What this means for you
If you are still using PHP 5.5 (or older), then you are using a version of PHP that has already reached its End of Life and is no longer supported by the PHP project. If you are using PHP 5.6, then you are using a version of PHP that will reach its End of Life two years from now. And while two years seems like a long time at first glance, migrating a legacy application to PHP 7 can take some time.
The outdated version of PHP you use may still be maintained by the vendor of your operating system. However, this maintenance is usually limited to critical security fixes and does not include the backporting of regular bug fixes. Furthermore, you are missing out on a lot of improvements that were made to PHP. We provide some interesting background information on PHP 7 in this presentation , and there is a lot more in-depth coverage in our eBook " PHP 7 Explained ".
What you should do
It is high time to think about upgrading your PHP stack to PHP 7, ideally to PHP 7.1. This should be a short-term goal for you.
Upgrading the version of PHP you use must not be a rare event you are afraid of. You must not think of upgrading your PHP stack as a "special project". You need to make upgrading the PHP version you use part of your normal operational procedure and align the upgrade cycle of your PHP stack with the release cycle of the PHP project. This should be a long-term goal for you.
Existing systems age primarily because technology evolves. In the long term, the secure and smooth operation of software is only possible on up-to-date systems.
We can support you in planning and implementing the migration of your software to PHP 8.
Frameworks, Components, and Tools
While PHP itself is the most important part of your PHP stack, it is not the only part of it. You should also make sure that you use actively supported versions of your framework as well as components and tools you rely on.
Sooner or later new versions of frameworks, components, and tools will no longer support PHP 5. Here is a list of popular projects for which I was able to find information on PHP 5 support:
- NEOS 3.0 will be released in January 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- PHPUnit 6 will be released in February 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- TYPO3 8 LTS will be released in April 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- PhpSpec 4.0 will be released in June 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- Laravel 5.5 will be released in July 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- Xdebug 2.6 will be released in July 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- Symfony 4.0 will be released in November 2017 and will not support PHP 5
- Zend Framework plans to support PHP 5 until PHP 5.6 reaches its End of Life
- Joomla! 5 is planned for 2019 and expected to not support PHP 5 anymore
- Drupal 9, which is still several years away, is expected to not support PHP 5 anymore
The release of a new version such as PHPUnit 6 does not mean, of course, that PHPUnit 5.7 stops working. Old versions such as PHPUnit 5.7 might even still receive bug fixes but new versions with new features require a new version of PHP.
 Deutsch
Contact
Deutsch
Contact
